Description
The PZEM-004T module is an integrated module designed for measuring electrical parameters in an AC circuit. It can measure voltage, current, power, energy, and other electrical parameters accurately. The sensor uses non-invasive current transformers (CTs) or current coils to measure the current flowing through a wire without the need for cutting or interrupting the circuit.
Features
- Measured Parameters: It can measure AC voltage, current, active power, active energy (kWh), frequency, and power factor.
- Operating Voltage: The module operates on an AC voltage range of 80V to 260V.
- Current Measurement: It can measure current up to 100A using a non-invasive current transformer (CT) coil that is typically included.
- Rated Power: The maximum rated power is 22kW.
- Communication Interface: It features a TTL serial data communication interface, allowing it to be easily interfaced with microcontrollers like Arduino, ESP8266, and Raspberry Pi. The newer Version 4.0 uses the Modbus-RTU protocol over RS485 for communication.
- Data Storage: The module includes a power-down data storage function to save cumulative energy data before a power loss.
- Energy Reset: A built-in button allows the user to clear the accumulated energy data.
- Connectivity: For communication with a PC or other devices lacking a TTL interface, a separate TTL to USB or TTL to RS232 adapter board is required.
- Software: PC software is often included with the module for displaying and analyzing the measured parameters.
Specifications
- Voltage Range: 80–260V AC, resolution 0.1V, accuracy ±1.0%
- Current Range: 0–100A (with external CT), resolution 0.01A, starting from 0.01A
- Power Range: 0–22kW, resolution 0.1W (under 10kW) or 1W (10–22kW), starting from 1W
- Energy Range: 0–9999kWh, resolution 0.001kWh (under 10kWh) or coarser for higher values
- Interface: TTL serial (5V logic), no display
- Dimensions: Approximately 63mm x 38mm x 18mm (PCB)
Note:
- This is an indoor module and can not be used outdoors.
- Load can be over rated power.
- Wiring can not be wrong.
Interfacing PZEM-004T Module with Arduino
Hardware Required
- Arduino Uno
- PZEM004T
- Breadboard
- Jumper wires
- AC load (e.g.: lamp)
Software Required
- PZEM-004T-v30 library
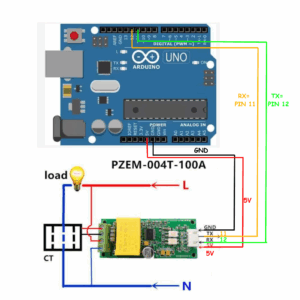
ZEM-004T Module Circuit Diagram & Connection
Connect the PZEM-004T’s 5V and GND to Arduino’s 5V and GND for power. Link TX (PZEM) → RX (Arduino pin 11) and RX (PZEM) → TX (Arduino pin 12) for serial communication.
Wire the live (L) and neutral (N) of your AC supply (120V/220V) to the PZEM’s AC input terminals (labeled “L” and “N”).
Caution: Isolate AC input (120/220V) wiring from Arduino circuits for safety.
Source Code/Program
Lets write an Arduino C++ Code to establish a Serial Communication between Arduino & PZEM-004T Energy Meter Module.
/*
Example of using one PZEM module with Software Serial interface.
================================================================
If only RX and TX pins are passed to the constructor, software
serial interface will be used for communication with the module.
*/
#include <PZEM004Tv30.h>
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
#if defined(ESP32)
#error "Software Serial is not supported on the ESP32"
#endif
/* Use software serial for the PZEM
* Pin 11 Rx (Connects to the Tx pin on the PZEM)
* Pin 12 Tx (Connects to the Rx pin on the PZEM)
*/
#if !defined(PZEM_RX_PIN) && !defined(PZEM_TX_PIN)
#define PZEM_RX_PIN 11
#define PZEM_TX_PIN 12
#endif
SoftwareSerial pzemSWSerial(PZEM_RX_PIN, PZEM_TX_PIN);
PZEM004Tv30 pzem(pzemSWSerial);
void setup() {
/* Debugging serial */
Serial.begin(115200);
}
void loop() {
Serial.print("Custom Address:");
Serial.println(pzem.readAddress(), HEX);
// Read the data from the sensor
float voltage = pzem.voltage();
float current = pzem.current();
float power = pzem.power();
float energy = pzem.energy();
float frequency = pzem.frequency();
float pf = pzem.pf();
// Check if the data is valid
if(isnan(voltage)){
Serial.println("Error reading voltage");
} else if (isnan(current)) {
Serial.println("Error reading current");
} else if (isnan(power)) {
Serial.println("Error reading power");
} else if (isnan(energy)) {
Serial.println("Error reading energy");
} else if (isnan(frequency)) {
Serial.println("Error reading frequency");
} else if (isnan(pf)) {
Serial.println("Error reading power factor");
} else {
// Print the values to the Serial console
Serial.print("Voltage: "); Serial.print(voltage); Serial.println("V");
Serial.print("Current: "); Serial.print(current); Serial.println("A");
Serial.print("Power: "); Serial.print(power); Serial.println("W");
Serial.print("Energy: "); Serial.print(energy,3); Serial.println("kWh");
Serial.print("Frequency: "); Serial.print(frequency, 1); Serial.println("Hz");
Serial.print("PF: "); Serial.println(pf);
}
Serial.println();
delay(2000);
}
This Arduino code reads power parameters from a PZEM-004T V3.0 energy meter using SoftwareSerial on pins 11 (TX) and 12 (RX). It retrieves and displays voltage, current, power, energy, frequency, and power factor on the Serial Monitor. If any value is invalid, it prints an error message. Readings update every 2 seconds.
From the Tools Menu, Select the Arduino Nano/UNO Board depending upon your board. Select the COM port and click on upload button to upload the code.
Once the code uploading is done the device is ready for testing. Power on the load now so that the load turns ON. Serial monitor should display something like this:
Custom Address:1 Voltage: 131.30V Current: 0.02A Power: 0.00W Energy: 0.003kWh Frequency: 50.3Hz PF: 0.00
Package includes: PZEM-004T AC Current Voltage Multimeter Module 80-260V 100A + Split Core Transformer WF4458037